Joe is generous with his time and energy, always willing to listen and give advice. His strength and courage inspire everyone around him.
One day, he confessed to me that he was not feeling well. I could tell something was wrong with him, but he didn’t want to talk about it. After weeks of worrying, I finally got him to see a doctor, who discovered Joe had a heart problem. Today he is better, but a miracle saved him.
In the USA, every 40 seconds, someone suffers a heart attack. A heart attack is the most common heart disease. It occurs when blood flows to the heart and part of it is blocked, often by a blood clot, a thick, almost solid mass that forms when blood dries.
Occasionally, the lump is called a coronary thrombosis or coronary occlusion, caused by the rupture or tearing of plaque in an artery. A heart attack is also known as a myocardial infarction, which can also occur when a coronary artery temporarily contracts or goes into spasm, slowing or cutting off blood flow to the heart.
There are three main symptoms of a heart attack. One is pressure or pain in the center of the chest, which lasts for a few minutes or goes away and returns. A second symptom is when the pain spreads to the shoulders, neck, or arms. A third symptom is chest discomfort, combined with dizziness or shortness of breath.
What is the difference between a heart attack and cardiac arrest? A heart attack occurs when a blocked artery interrupts blood flow to the heart, but the heart usually continues to beat.
What are the causes of cardiac arrest? Specific causes of cardiac arrest arrhythmia, such as irregular heartbeats, can short-circuit the heart’s electrical system. A quarter of heart attacks cause cardiac arrest, either immediately or one to two hours later.
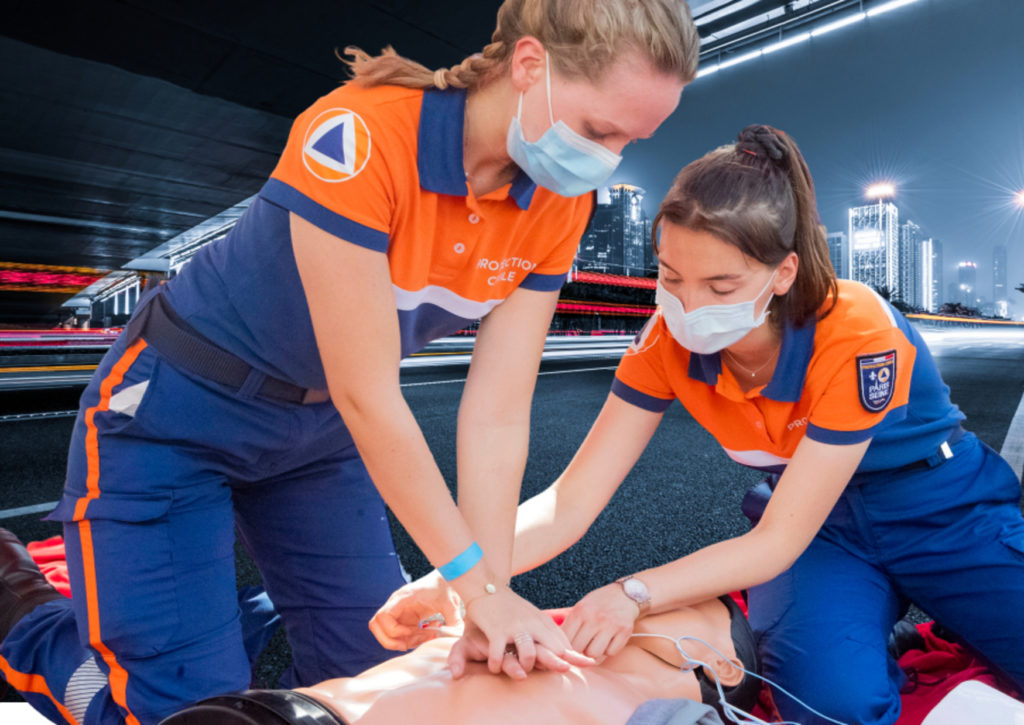
Can cardiac arrest be treated? In most cases, the only way to treat cardiac arrest is to shock the patient using a defibrillator.